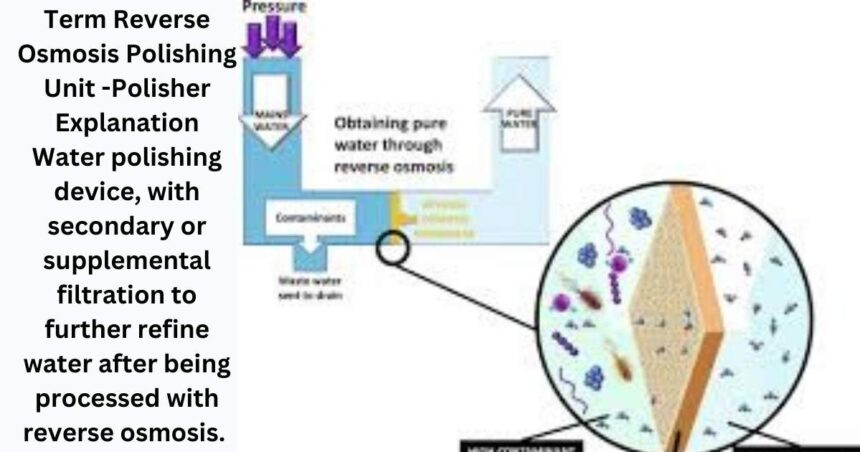
Term Reverse Osmosis Polishing Unit -Polisher Explanation Water polishing device, with secondary or supplemental filtration to further refine water after being processed with reverse osmosis. Reverse osmosis works well in multiple areas of contaminant removal, but the polisher adds one final purification step to ensure that the water output meets specific standards necessary for particular industries or applications.
Reverse Osmosis (RO) Explained
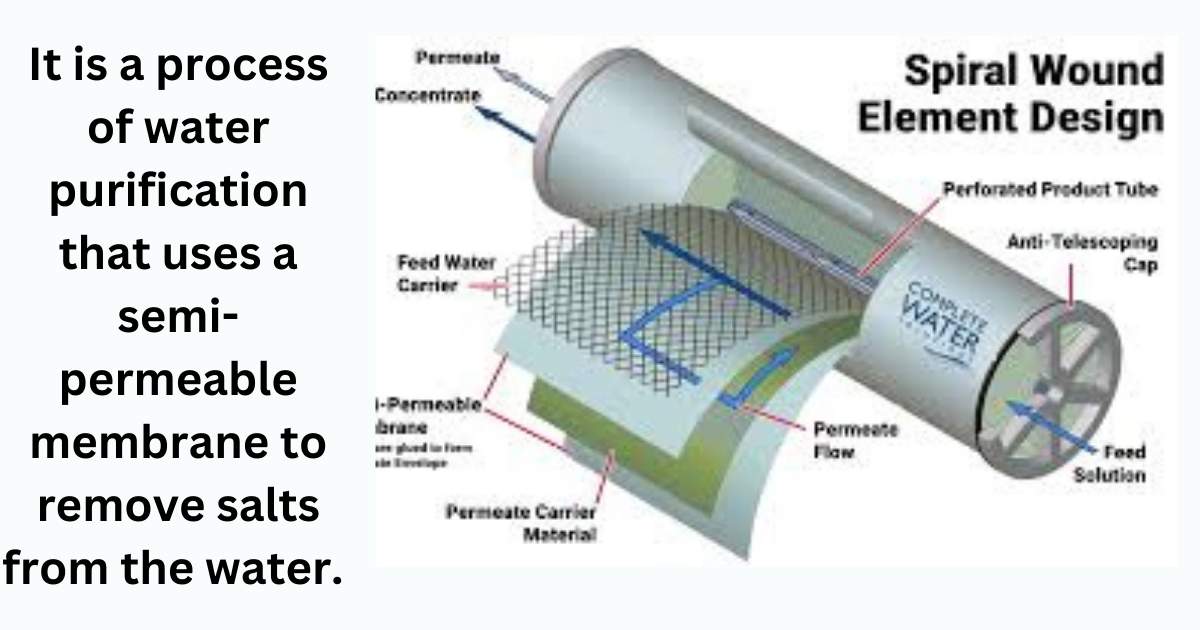
Understanding what does reverse osmosis mean Before we jump into an Overview of a RO polisher it is important to find out How Reverse Osmosis Works RO simply means Reverse Osmosis, it is a process of water purification that uses a semi-permeable membrane to remove salts from the water. The membrane will only allow the water molecules to pass and filter out anything else in the way including:
- Dissolved salts and minerals
- Organic molecules
- Bacteria and viruses
- Heavy metals
This stage, when done properly, can eliminate 90–99% of contaminants in the water stream.
This is not always good enough for applications that demand ultrapure water, but this reverse osmosis process on its own. Such finer impurities may still exist (particularly at trace levels). This is where the RO polisher will help.
What Does a RO Polisher Do?
Hard Water enters the Water purifier and the RO polisher refines the water after the RO filter. The final polish of an RO polisher can be done with different means depending on design and application (deionisation, activated carbon filtration, or some specialized filters targeting specific contaminants that have been missed of not thoroughly removed by the RO system)
Key Roles of a RO Polisher:
Even though RO systems filter a lot of water, there are still trace amounts of dissolved salts, organic compounds, and other fine-particles that remain in the water. Any remaining fragments are targeted by a polisher and the water is, ultima-pure.

Additionally, they are frequently found in household applications, particularly for drinking water: RO polishers can add carbon filters to improve taste and smell that could be left over from reverse osmosis. This is great for when RO water might taste a little flat or metallic because the membrane does filter stuff but can impart its tastiness too.
- Strips Dissolved Gases: Some dissolved gases (e.g. carbon dioxide) can pass through the RO membrane which may alter the pH or taste of filtered water When a polisher pH goes to work on these gases it neutralizes them, and can provide water that is closer to being neutral under stable conditions.
- Deionization (DI) for Ultra-Pure Water- a common system in industries that need ultra-pure water such as pharmaceuticals, laboratories or semiconductor manufacturing is the use of deionization. This technique is one that uses ion exchange resins to remove cationic and anionic ions from the water. Water conductance can be reduced even further by removing these charged groups resulting in ultrapure with very low conductivity called deionized water (DI).
- Provide Uniform Water Quality: The polisher helps to deliver uniform quality water throughout supply pipelines which is a must in industries where extreme precision matters the most. This second level of filtration ensures that fluctuations in water quality due to changes in source water conditions or the life-cycle performance of the primary RO system will be removed.
Types of RO Polishing Systems
The kind of RO polisher used depends both on the application and in what final water quality is needed Here are some common types of RO polishers:
- Deionization (DI) Polisher
Das deionisiert die meisten Reinwassermedien became quarliadivaDeionisation ist in der Regel die verwendeteste Methode zur Erzeugung von ultrareinem Wasser. In a DI polishers, the water then passes through ion-exchange resins that remove All cations (positive ions like sodium (Na⁺), calcium (Ca²⁺), and magnesium Mg²⁺), and anions (Negative ions like chloride Cl⁻ and sulphate SO₄²⁻ apart. The result is an almost total elimination of all ionized species and so is perfect for laboratory, electronics manufacture or medical applications.
- Activated Carbon Polisher
Most residential and commercial dry cleaners use this type of polisher, particularly for drinking water. The activated carbon filter will remove organic pollutants, chlorine and chloramines that influence the flavor, odor or safety of the water. This is very effective for the adsorption of chemicals and VOC´s that might be left even after the Reverse Osmosis system has done its work.
- UV Sterilization Polisher
Ultraviolet (UV) sterilization is employed in cases of high hygiene, the use of RO polishers will followed by UV to kill any germs existing in the final product. Should sterility be required, for example in pharmaceutical or medical applications this might raise a great additional value.
- Electrodeionization (EDI)
Electrodeionization (EDI) is sometimes used alone to make ultrapure water on large-scale industrial or laboratory systems.Edi-after-ro. EDI uses ion-exchange resins and electricity to continuously remove ions from water — down to very low levels of total dissolved solids (TDS) into the high purity range. The big benefit with EDI is that there is no requirement for chemical regeneration, it means it can be greener.
- Mixed-Bed Resin Filters
So, in many cases, these filters are used directly after RO for ionic contamination removal and nearly always paired resin technologies (mixture of Cation exchange resins and Anion exchange resins) for ultra-pure water applications. Mixed-bed resins are quite effective, and it is commonly used in semiconductor production, power generation, lab-scale applications etc.
Applications of RO Polishers
Residential Water Systems: A number of domestic water filtration systems use a RO polisher to enhance flavor and safety of drinking water. The most popular kind of polisher that are in use on these systems is activated carbon.
While ultra-pure water: UV water is vital to countless applications, in the medical and pharmaceutical sectors the purity requirements are so strict that even trace contaminants can mean failed drug production or patient care. Especially for DI systems, they are essential in use of RO polisher which is must to have in order to meet the water quality requirements.
Laboratories and Research: Ultra Pure Water Required for Experiments, Cleaning of Equipment and Reagent Preparation in Scientific Research. Because even low levels of impurity can affect results, water is not uncommonly run through an RO system, often followed with a DI or mixed-bed resin polish.
Semiconductor: Fabrication represents extremely low conductivity or ultrapure water with a very few dissolve solids for semiconductor manufacturing. The EDI or mixed-bed resin polishers are combined with RO systems to fully comply with stringent purity requirements found in the pharmaceutical industry.
Food and Beverage: Beverage Production & Food Processing industries use high-volume RO polishers to maintain water free of off-tastes, odors, and impurities which would affect the taste of your products.
Benefits of Using an RO Polisher
Ultra-Pure Water: An RO polisher ensures that no unwanted trace contaminants are left in water for the highest purity applications.
Residential systems: In residential installations, polishers improve taste, meaning homeowners are more likely to consume clean water.
Variety Of Types: RO polishers are available in various types that may be customized to the water purity level you need within a specific industry or at home.
Reliability: Using a polisher ensures that water quality remains consistent regardless of how the feedwater conditions vary or how efficiently the primary RO system processes water.
Conclusion
An RO polisher is essential for further enhancing the quality of water post-reverse osmosis process and can be used in applications where ultra-pure water is also needed. Polishers are used in everything from household drinking water systems to ultra-pure industrial applications to quality-safeguard the final output, ensuring that it meets specific purity requirements (or even just taste or safety standards).
The type of RO polisher employed can vary from basic activated carbon filters or more advanced deionization and EDI systems depending on the expected level of treatment needed to remove specific contaminants.
The RO polisher is essentially the last line of defense that ensures the absolute highest quality water available for numerous applications.